Vestaro GmbH
Although millions of electric cars and plug-in hybrids from many manufacturers are already on the road, there are still no generally recognized standards for the individual components in terms of service life or materials used. Moreover, the vehicles themselves are under rapid development. Currently, much attention is being paid to increasing the range of electric cars. This can be achieved by improving battery storage capacity and through efficient energy recovery. A second approach is to reduce the weight of the individual components, in order to reduce the energy needed to overcome driving resistance (tire rolling, inclination, and acceleration). The effect of weight reduction on the efficiency of the drive depends on the propulsion strategy of the electric vehicle. A consortium consisting of Lorenz Kunststofftechnik, Forward Engineering, Evonik, LION Smart, Vestaro, and Minth has developed a promising and effective solution to help improve efficiency through lightweight construction. In late 2019, work started on a brand-independent, low-cost battery housing solution in different sizes for electric vehicles. The result of the cooperation was a significant weight reduction of the battery by about 10% over other commonly used material combinations, without sacrificing any mechanical properties. In addition, the glass fiber-reinforced epoxy SMC – purpose-developed for the battery housing – meets all fire resistance requirements and is easy to work, even with complex geometries. The entire concept has been tested and shown to be suitable for series production and is safe even under extreme conditions.
Compared to the long developmental history of the internal combustion engine, e-mobility is still a very young technology. Nevertheless, many manufacturers around the world are launching a wide variety of vehicles onto the market. These vehicles differ greatly, not only in design and equipment, but also in construction and technology. This has led to a wide range of materials and component designs. But there are efforts to standardize individual assemblies of vehicles and develop a cross-market component standard. “Under the leadership of VESTARO GmbH, in 2019 we joined a cooperation with Forward Engineering, Evonik, and LION Smart, with the goal of developing a series-suitable battery concept for BEV models,” reports Peter Ooms, COO of Lorenz Kunststofftechnik GmbH. “Our main focus was the formulation for a glass fiber-reinforced epoxy SMC that meets all requirements for safety and workability and can also be returned to the material cycle.” In 2021, Minth GmbH, the European headquarters of the Chinese automotive supplier Minth Group, also joined the consortium.
Development of a new glass fiber-reinforced epoxy SMC
Components used in lightweight construction for hybrid and electric vehicles, such as battery housings, must not only be low in weight, but also exhibit high rigidity and strength. Carbon fiber-reinforced SMC materials can be used for this purpose, but they are very expensive and typically non-recyclable. Beyond that, there were few available materials with the necessary attributes, as they were either too heavy or had insufficient mechanical strength. “For the battery housing, we used Evonik’s VESTALITE®S epoxy hardener to develop a new SMC with a density between 1.5 and 1.7 g/cm³,” explains Ooms. “It has outstanding properties, like a bending strength of > 350 MPa, a flexural modulus of elasticity of > 18,500 MPa, and an impact resistance of > 150 kJ/m2.” By using an epoxy resin instead of the usual polyester resin, it was possible to eliminate other problems that normally arise in working with glass fiber-reinforced SMC materials. “With VESTALITE®S Epoxy Lorenz SMC, the molding material can be worked into complex geometries without adhering to the mold,” notes Ooms. The formulation has better mechanical properties than conventional SMC materials and features a very good fiber course in the molding process. Moreover, Lorenz has an established process for recycling glass fiber-reinforced SMC materials, which is an important consideration given the sustainability requirements in the automotive industry.
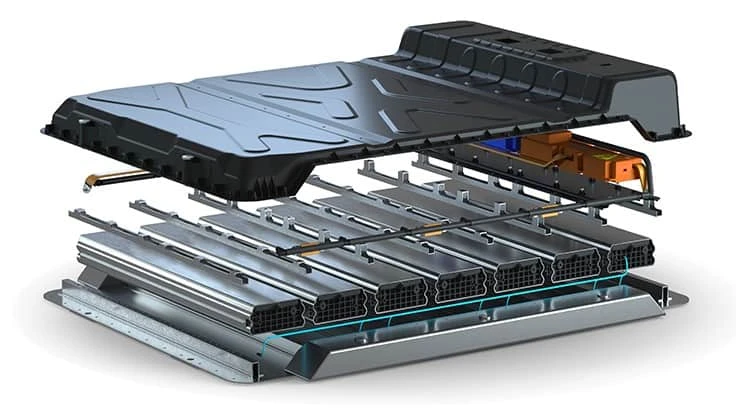
Substructure and battery module
For the supporting structure of the battery housing, the cooperation partners chose aluminum as a proven lightweight material. The general goal for the supporting structure was simple geometries and thus lower production costs. “The bottom plate is the basis of the entire battery construction and has cross-members that the battery module is mounted on. The carrier plate for the battery management system is also attached to the aluminum base,” reports Philipp Taschner, Project Engineer of VESTARO GmbH. Two aluminum deformation elements provide the necessary side impact protection through absorption. The module alignment of the battery cells enables separation of the electric poles, which provides higher safety in the event of a crash and enables easy cooling.
LION Smart’s supercell concept was used for the batteries. “The design of the battery cells with a low number of components is intended for fully automated, cost-efficient production,” explains Taschner. “In addition, the battery design is particularly safe, as the individual cells are enclosed in a non-flammable dielectric coolant.” This not only provides higher safety, it also ensures a constantly low average temperature within the battery, which reduces cell aging. The modular series connection design of the battery also allows flexibility in the number of modules, with a very low overall height of 90 mm.

@Vestaro GmbH
The modular series connection design of the battery also allows flexibility in the number of modules, with a very low overall height of 90mm
Latest from EV Design & Manufacturing
- Powering homes with EV batteries could cut emissions, save thousands of dollars
- Meviy introduces stainless steel passivation option for CNC, sheet metal parts
- December Lunch + Learn webinar with Fagor Automation
- December Lunch + Learn webinar with LANG Technik + Metalcraft Automation Group
- EVIO makes public debut with hybrid-electric aircraft
- Redesigned pilot step drill triples performance
- Green Energy Origin expands battery electrolyte manufacturing in North America, Europe
- What’s next for the design and manufacturing industry in 2026?